By Dr Carmen Lorente, DVM, PhD, DipECVD. EBVS® European Specialist in Veterinary Dermatology
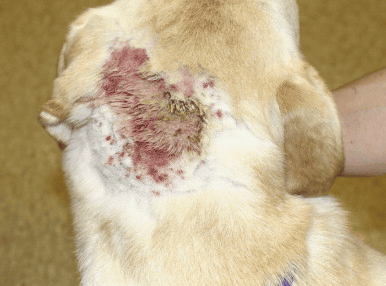
From Stephen D. White, in Canine and Feline Infectious Diseases, 2014
Most cases of canine pyoderma are caused by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Despite Staphylococci having a relatively predictable pattern of antimicrobial sensitivity and often responding to an empirical selection of treatment, bacterial resistance is becoming more and more frequent, making culture and sensitivity tests necessary. In some countries, the use of systemic antibiotics is recommended only after culture and antibiogram have been performed.
WHAT ANTIBIOTICS CAN BE USED EMPIRICALLY TO TREAT SUPERFICIAL PYODERMA?
Only first line antibiotics should be used empirically. These include amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, cephalexin, cefadroxil, lincomycin, and clindamycin.
In some countries, the use of systemic antibiotics is strictly regulated and is recommended only after culture and antibiogram have been performed.
WHEN IS IT NECESSARY TO PERFORM A BACTERIAL CULTURE AND ANTIMOCROBIAL SENSITIVITY TESTING?
Bacterial culture and antimicrobial sensitivity testing are necessary in the following situations:
- Infections not resolving with empirical antibiotic therapy.
- Life-threatening infections as it is crucial for the initial antibiotic treatment to be effective
- Clinical lesions consistent with deep pyoderma.
- No consistency between clinical signs and cytology.
- Rod-shaped bacteria seen on cytology, as their antibiotic sensitivity may vary and may be limited.
- Immunosuppressive disease or treatment.
HOW TO OBTAIN MATERIAL FOR BACTERIAL CULTURE?
- Collect samples from representative lesions:
- Intact pustules -> elevate the surface with a sterile needle and sample with a sterile swab.
- Crusting pustules or crusts -> collect material from under the crust using a sterile swab
- Margin of epidermal collarettes -> rotate a sterile swab under the exfoliating margin (wet the swab with sterile saline solution).
- Ulcers -> scrape or swab the leading edge of the ulcer.
- Deep pyoderma -> tissue biopsy sample.
- Avoid surface contamination.
- Use a sterile swab with transport medium.
- Include clinical history with the submitted sample
- Inform the lab if the animal has recently been or currently is on antibiotics. If possible, samples should be taken 48 hours after the last dose of oral antibiotics.
INTERPRETATION OF THE RESULTS
The isolate is reported as susceptible, intermediate or resistant. Isolates with intermediate susceptibilities should be regarded as resistant.
How to choose an antibiotic after the sensitivity test?
Choose an antibiotic from the pool of susceptible results that belongs to the lowest group line:
- First-line drugs: they are the first choice whenever they are susceptible.
- Second-line antibiotics are not appropriate for empirical antibiotic treatment. They should only be used when first-line drugs are not effective.
- Third-line antibiotics to be used when first- or second-line antibiotics are not effective.
